
Batch culture cultivation Download Scientific Diagram
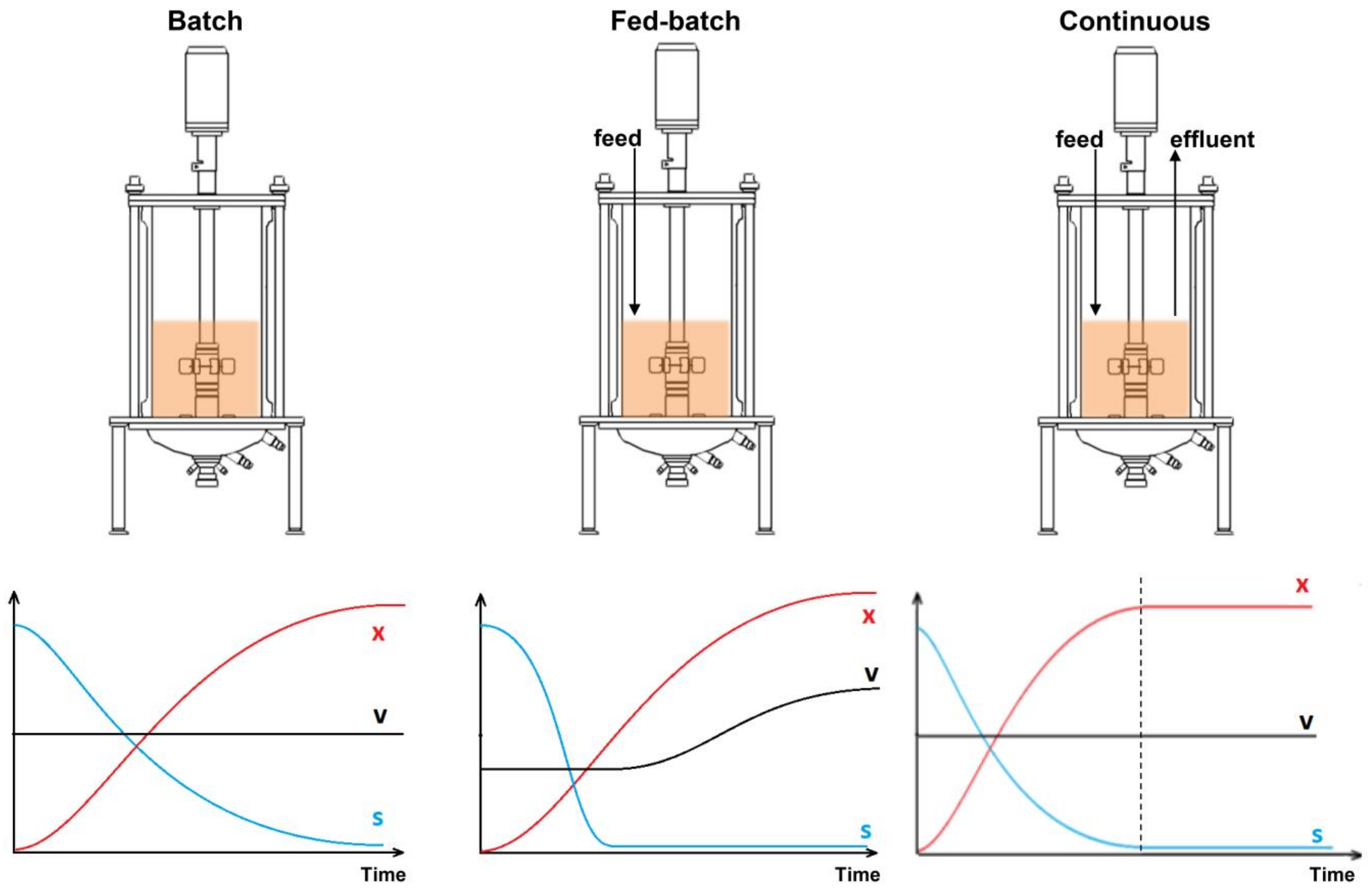
Batch culture systems are widely applied because of their simplicity and flexibility, allowing to change species and to remedy defects in the system rapidly. Although often considered as the most reliable method, batch culture is not necessarily the most efficient method. Batch cultures are harvested just prior to the initiation of the.
The Difference Between Batch, Fedbatch and Continuous Processes (2022)
The fed-batch culture ran for. 12 days and reached a peak density of 21 x 106 cells/mL on day 9. Our perfusion culture ran the longest and reached the highest density of all bioprocess modes by day 15. A batch culture takes significantly less run time than a fed-batch or perfusion and is the easiest process to execute.
The Difference Between Batch, Fedbatch and Continuous Processes Blog
Download scientific diagram | Schematic diagram of batch culture. from publication: Metabolic pathways of hydrogen production in fermentative acidogenic microflora | Biohydrogen production from.
Difference between Batch and Continuous Fermentation Definition, Structure, Advantages and Key
Continuous Culture Definition. Continuous culture is a continuous process where nutrients are continually added to the bioreactor and the culture broth (containing cells and metabolites) is removed at the same time. The volume of the culture broth is constant due to a constant feed-in and feed-out rate (i.e consumed nutrients are replaced and.
Frontiers Optimizing a FedBatch HighDensity Fermentation Process for Medium ChainLength
A bacteriophage is a type of virus that infects bacteria. It does so by injecting genetic material - either DNA or RNA - which it carries enclosed in an outer protein capsid. To enter a host cell, bacteriophages attach to specific receptors on the surface of bacteria, including lipopolysaccharides, teichoic acids, proteins, or even flagella.

Figure 1 from Optimal control of a fedbatch fermentation process using model
Fed-batch culture is a modified batch culture method or an intermediate of batch and continuous fermentation techniques. Like batch culture, products of the fed-batch culture are harvested in batches, i.e. after the batch time. However, the substrate is added periodically throughout the cultivation, like the continuous fermentation method.
PPT MIC 303 INDUSTRIAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY PowerPoint Presentation ID6396145
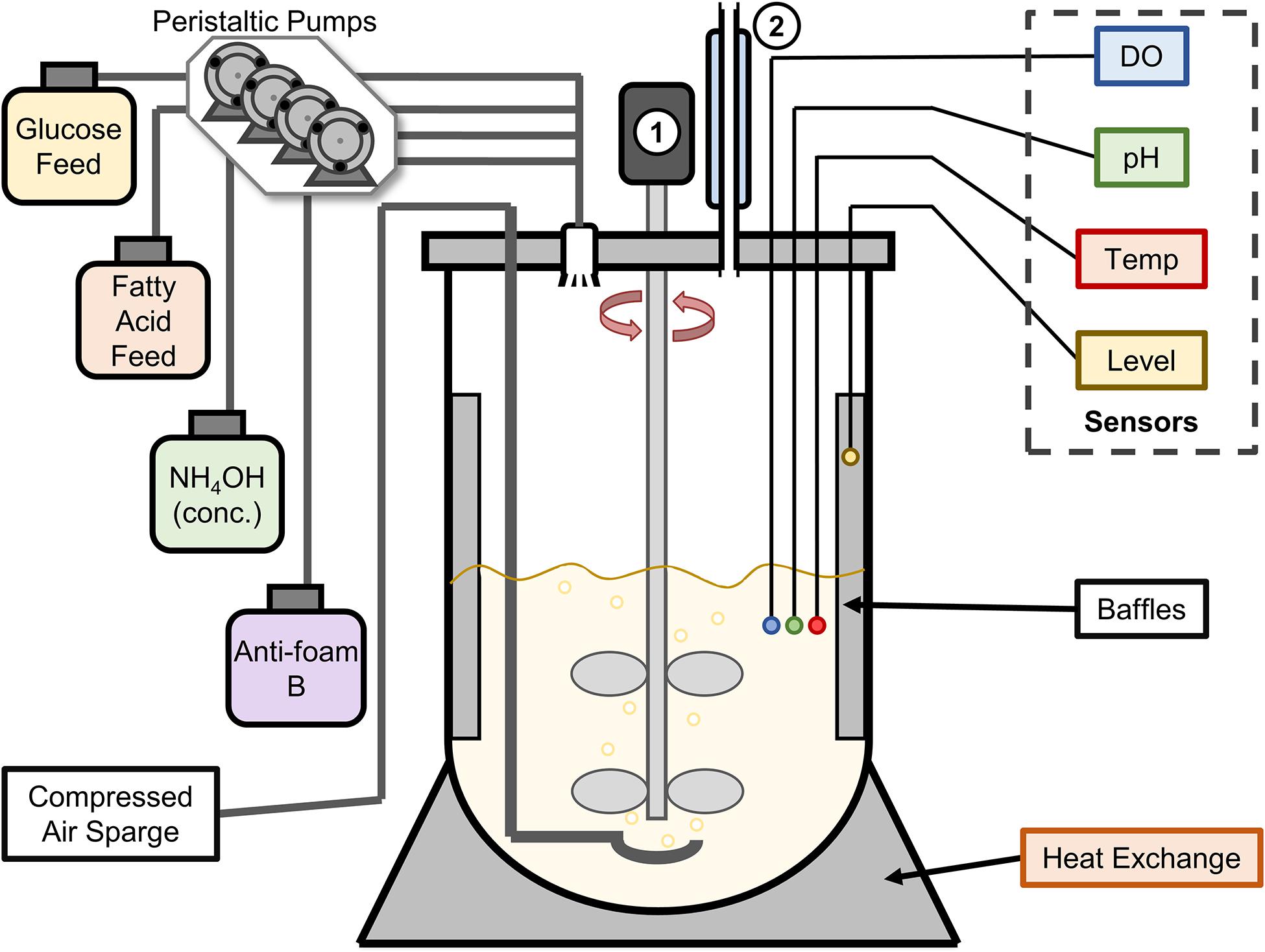
The Choice of Bioreactor Affects Many Aspects of Bioprocessing. Product concentration and purity. Degree of substrate conversion. Yields of cells and products. Capitol cost in a process (>50% total capital expenses) Further Considerations in Choosing a Bioreactor. Biocatalyst. (immobilized or suspended) Separations and purification processes.

Simplification of FedBatch Processes with a SingleFeed Strategy BioProcess
Highlights • Fed-batch culture based on pH changes increased 90.6% biomass of H. pluvialis. • This strategy enhanced carbon metabolism by elevating pyruvate and ace-CoA contents. • Astaxanthin productivity was increased to 4.5 mg L −1 d −1. • Acetate was beneficial for Rubisco activity in H. pluvialis than glucose. Abstract

Setup of a concentrated perfusion or fedbatch setup using the... Download Scientific Diagram
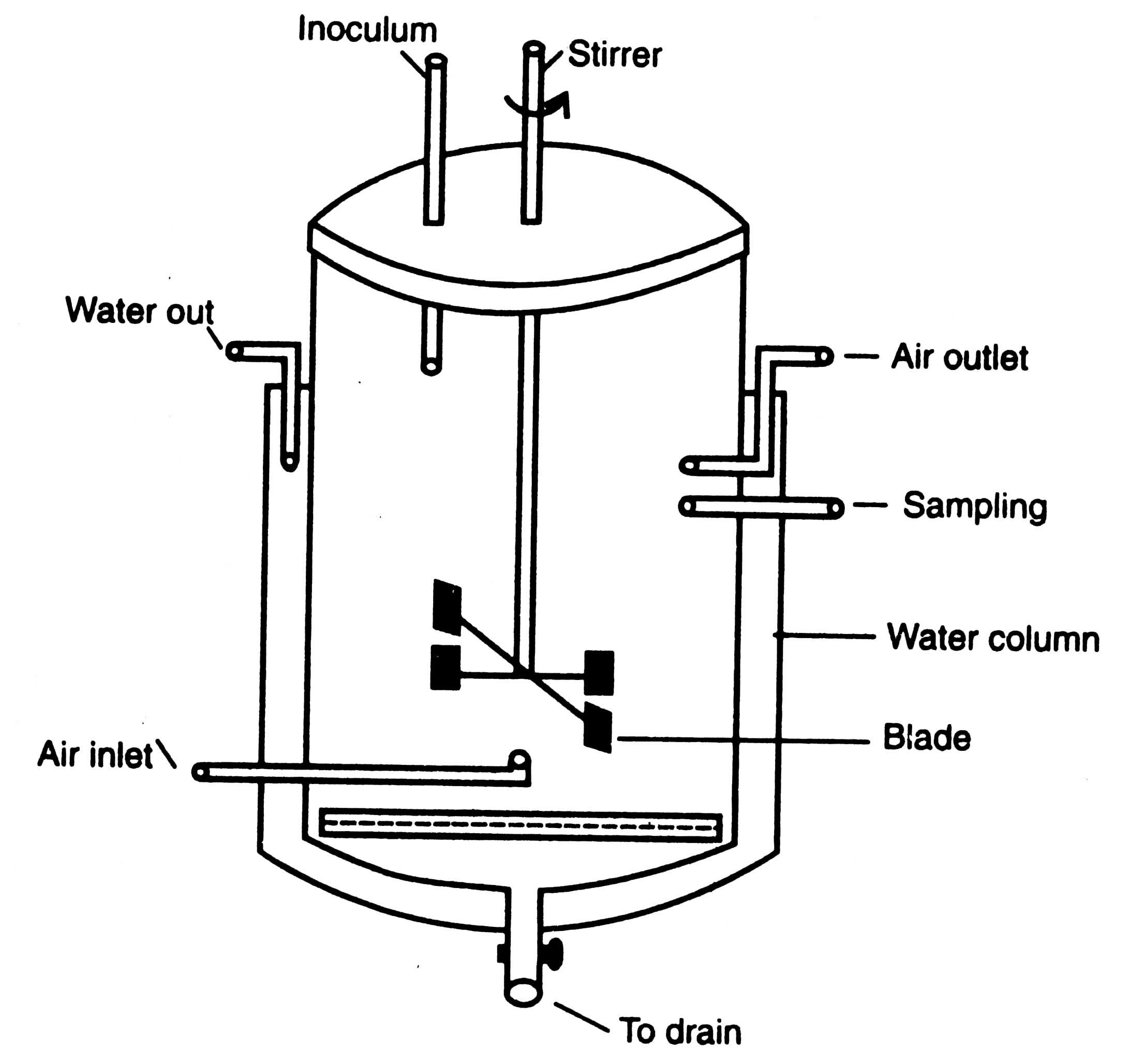
In batch culture, all the medium components are placed in the reactor at the start of cultivation except for atmospheric gases, acid or base for pH control, and antifoaming agents. There is a continuous change in the nutrient concentrations over time, and the system remains unsteady. Fed-Batch Culture Definition

23 Difference Between Batch and Continuous Culture
Overview Feed automation Perfusion The addition of nutrients and removal of by-products to and from the culture medium, respectively will affect the cell density and viability, the bioprocess duration, and as a result, the product titer, yield, and cost.

Schematic diagram of the bioplastics in the batch culture experiment,... Download Scientific
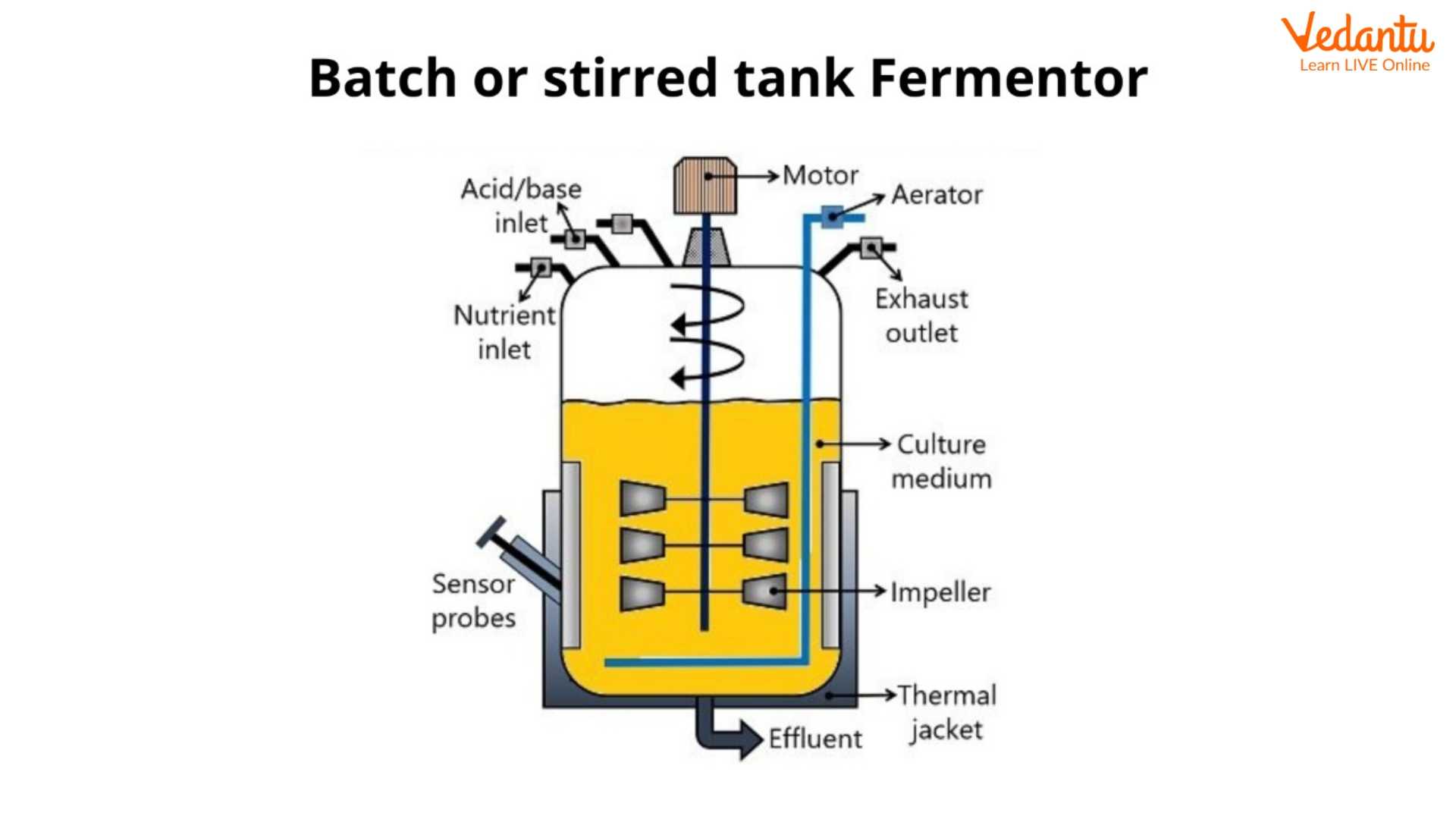
Batch Culture or Batch Fermentation: A batch fermentation is regarded as a closed system. The sterile nutrient culture medium in the bioreactor is inoculated with microorganisms. The incubation is carried out under optimal physiological conditions (pH, temperature, O 2 supply, agitation etc.).
Cultures of Biotechnological Importance in
4.1 Batch Culture. The cell concentration (or other corresponding parameters) is measured at two points in the exponential phase when the biomass is linearly changed, and the specific growth rate was calculated as follows: μ = (ln D n - ln D n-1)/(t n - t n-1) where D n and D n-1 represent the biomass at t n and t n-1 respectively (usually expressed as cell density, dry weight or.

Bioreactor Fedbatch culture Turbidostat Chemical reactor Chemostat, cell culture flask, angle
Bacterial cultures can be maintained in a state of exponential growth over long periods of time using a system of continuous culture (Figure 4), designed to relieve the conditions that stop exponential growth in batch cultures. Continuous culture, in a device called a chemostat, can be used to maintain a bacterial population at a constant.

Batch Normalization EXPLAINED! YouTube
Batch culture has the following mention advantages: Reduced risk of contamination or cell mutation as the growth period is short. Lower capital investment when compared to continuous processes for the same bioreactor volume. More flexibility with varying product/biological systems.

Continuous Culture In Fermentation Rezfoods Resep Masakan Indonesia
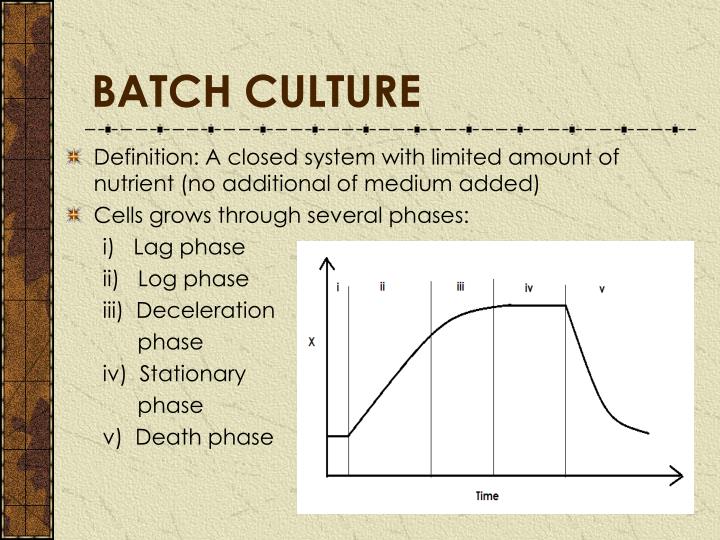
A typical bacterial growth curve consists of four phases: lag, log, stationary, and death. This bacterial growth curve reflects the events in the bacterial populations when grown in a closed system of microbial culture of fixed volume (i.e., batch culture). This classical growth curve for batch cultures of bacteria was proposed by Buchanan (1918).
Fermentation Free FullText Model Predictive Control—A Stand Out among Competitors for Fed
Principle Batch Fermentation Process Growth Curve in Batch Culture Advantages Disadvantages Applications Conclusion Batch Fermentation Definition It refers to a technique in which microbial cells grow and multiply to convert substrates into products. Batch fermentation is performed using the stirred tank fermentor.